Education is the foundation of every nation's growth and development. However, the Indian education system has been criticized for its shortcomings, ranging from inadequate infrastructure and limited access to quality education to a lack of innovation and ineffective teaching methodologies. This article aims to examine the two critical areas where the Indian education system lacks: 1. Education and 2. System. By analyzing the root causes, consequences, and potential solutions, we will provide insights into the pressing need for reform in the education system.
1. The Indian Education System: Lacking Education
Education is a fundamental right and a powerful tool for individual growth and national development. However, the Indian education system faces significant challenges in providing quality education to all its citizens. This essay aims to delve deeper into the specific aspects where the Indian education system lacks in terms of education. We will explore issues such as access to education, quality of education, outdated curriculum, and the need for a more holistic approach to learning.
1.1. Access to Education:
One of the primary challenges faced by the Indian education system is ensuring access to education for all. Many children, particularly those from marginalized communities and rural areas, still struggle to enroll in schools and complete their education. Factors such as poverty, gender inequality, inadequate infrastructure, and distance from educational institutions create barriers that impede access to education. Efforts must be made to bridge this gap through initiatives like improving school infrastructure, providing transportation facilities, and implementing inclusive policies to address the specific needs of marginalized communities.
1.2. Quality of Education:
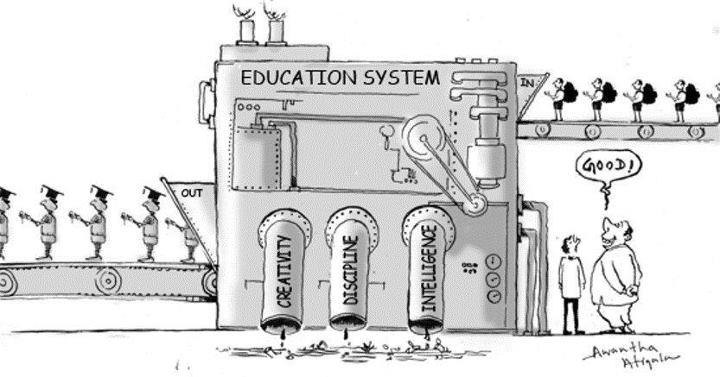
While access to education is crucial, the quality of education provided is equally important. The Indian education system often fails to deliver a high standard of education, resulting in a lack of necessary skills and competencies among students. The emphasis on rote learning, outdated teaching methods, and a focus on examinations rather than practical application hinders the development of critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills. To improve the quality of education, there is a need for curriculum reforms, teacher training programs, and the integration of experiential learning methodologies to foster a more holistic and student-centered approach to education.
1.3. Outdated Curriculum:
Another significant issue is the outdated curriculum that does not align with the evolving needs of society and the job market. The current curriculum often lacks real-world relevance and fails to equip students with the necessary skills for the modern workforce. There is a need to revise and update the curriculum to incorporate interdisciplinary subjects, digital literacy, life skills, and vocational training. This will ensure that students receive a well-rounded education that prepares them for the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century.
1.4. Holistic Approach to Learning:
The Indian education system often focuses solely on academic knowledge, neglecting the holistic development of students. Education should go beyond textbooks and examinations to encompass physical, emotional, social, and ethical aspects of growth. Incorporating co-curricular activities, sports, arts, and character-building programs can nurture well-rounded individuals. Additionally, the promotion of values, ethics, and empathy should be integrated into the education system to cultivate responsible and compassionate citizens.
The lack of education within the Indian education system manifests in various forms, including limited access to education, poor quality of education, an outdated curriculum, and the absence of a holistic approach to learning. Addressing these shortcomings requires a comprehensive approach that focuses on equitable access, improving the quality of education, updating the curriculum, and promoting holistic development. By providing inclusive and high-quality education, India can empower its citizens to realize their full potential, contribute to the nation's growth, and create a more equitable and prosperous society.
2. The Indian Education System: Lacking System
A well-functioning education system requires a robust and effective framework that ensures accountability, transparency, and innovation. However, the Indian education system faces significant challenges in terms of its structure and system. This essay aims to explore the specific aspects where the Indian education system lacks a coherent and efficient system. We will examine issues such as infrastructure deficiencies, ineffective teaching methodologies, centralized regulations, lack of autonomy, and the need for educational reforms to establish a more effective and responsive system.
2.1. Inadequate Infrastructure:
The Indian education system often grapples with inadequate infrastructure, particularly in rural and economically disadvantaged areas. Lack of proper school buildings, classrooms, libraries, laboratories, and other essential facilities hampers the learning environment and limits students' educational opportunities. Addressing this issue requires substantial investment in improving infrastructure, ensuring access to basic amenities, and creating a conducive environment for learning.
2.2. Ineffective Teaching Methodologies:
The traditional teaching methodologies employed in the Indian education system often focus on rote learning and memorization, which hinder critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity. Teachers primarily rely on lecture-based instruction, limiting student engagement and active learning. The system needs a shift towards student-centered pedagogies that encourage experiential learning, interactive discussions, and project-based approaches. Teacher training programs should also emphasize innovative teaching methods that foster independent thinking and lifelong learning skills.
2.3. Centralized Regulations:
The Indian education system suffers from a centralized regulatory framework that restricts institutional autonomy and inhibits innovation. Policies, regulations, and curriculum decisions are predominantly made at the central or state levels, leaving limited room for flexibility and adaptation at the local level. This lack of autonomy hampers institutions' ability to cater to the specific needs of students, communities, and industries. Decentralizing decision-making processes and empowering educational institutions with more autonomy can encourage innovation, experimentation, and customization to meet local needs effectively.
2.4. Lack of Accountability and Transparency:
The lack of accountability and transparency in the Indian education system is a significant concern that hampers its effectiveness and undermines public trust. There are major issues, including the absence of clear performance metrics, corruption and malpractice, and limited public access to information.
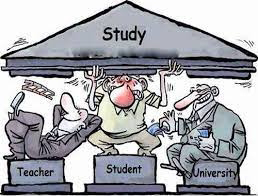
The Indian education system's dual shortcomings of education and system are hindering the nation's progress and development. The lack of access to quality education and the absence of a structured framework has resulted in a significant skill gap between education and employment, limiting the potential of individuals and the nation as a whole. To address these challenges, reforms are necessary to provide quality education to all students, irrespective of their socio-economic background. Additionally, a structured and effective system is required that ensures accountability, transparency, and innovation. By bridging the gap between education and system, we can empower the future generation of India to achieve their full potential and contribute to the nation's growth and development.
Hope this blog gave you a different insight to our current education system.












Very nice research 👌👌
ReplyDeleteKeep it up